Carbon Footprint
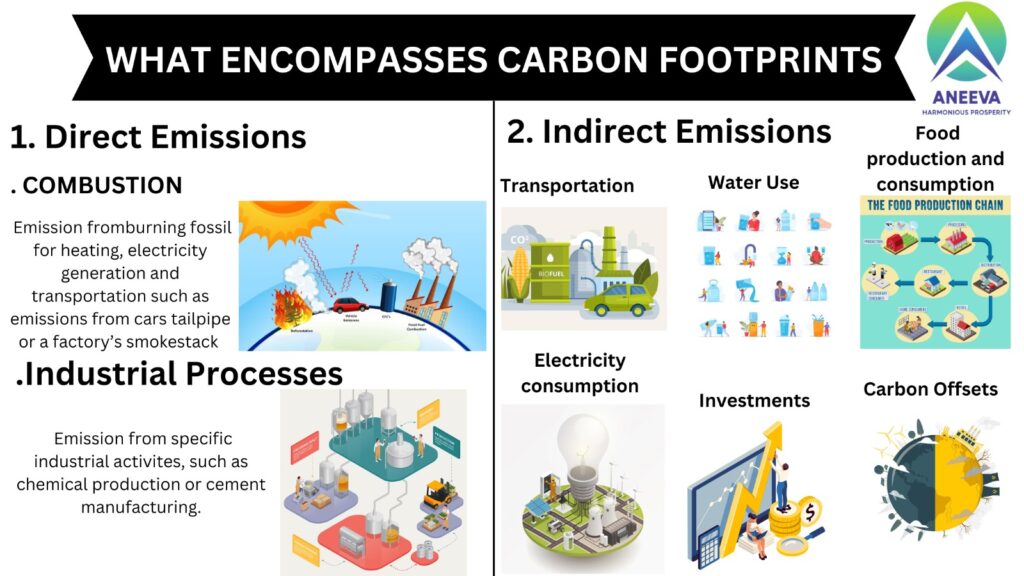
Defining Carbon Footprint A carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), that are emitted directly or indirectly by human activities. This includes emissions from burning fossil fuels for energy, transportation, and industrial processes, as well as emissions resulting from the production and consumption of goods and services. Relevance and Importance Understanding and reducing our carbon footprint is crucial in the fight against climate change. High levels of carbon emissions contribute to global warming, leading to extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems and human societies. Addressing carbon footprints is vital for sustainable development and environmental stewardship. Types and Categories Individual Carbon Footprints Individual carbon footprints encompass the emissions generated by personal activities such as driving, home energy use, diet, and travel. Corporate Carbon Footprints Corporate carbon footprints involve emissions from business operations, including manufacturing, transportation of goods, energy use in offices, and waste production. National Carbon Footprints National carbon footprints aggregate the emissions of an entire country, taking into account industrial activities, transportation networks, energy production, and consumption patterns. Symptoms and Signs Environmental Indicators Global Warming: Increase in Earth’s average surface temperature. Extreme Weather: More frequent and severe weather events like hurricanes, droughts, and floods. Melting Ice Caps: Accelerated melting of polar ice and glaciers. Rising Sea Levels: Expansion of seawater due to warming and melting ice. Societal Indicators Health Impacts: Increased respiratory problems due to air pollution. Economic Costs: Damage to infrastructure and agriculture, leading to financial losses. Migration: Displacement of communities due to environmental changes. attis, pulvinar dapibus leo. Causes and Risk Factors Biological Factors Human Population Growth: Higher population leads to increased demand for resources and higher emissions. Animal Agriculture: Livestock production generates significant methane emissions, a potent GHG. Environmental Factors Deforestation: Reduces the number of trees that can absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Urbanization: Expands areas with high energy consumption and GHG emissions. Lifestyle Factors Energy Consumption: Use of fossil fuels for heating, cooling, and electricity. Transportation: Reliance on cars, planes, and ships powered by fossil fuels. Diet: High meat consumption leads to higher carbon emissions compared to plant-based diets Diagnosis and Tests Carbon Footprint Calculators Online tools that estimate an individual’s or organization’s carbon footprint based on their activities and consumption patterns. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) Comprehensive studies that evaluate the potential environmental effects of proposed projects or policies, including their carbon footprints. Lifecycle Analysis (LCA) Assessment of the environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product’s life, from raw material extraction through production, use, and disposal. Treatment Options Renewable Energy Sources Solar Power: Harnessing energy from the sun. Wind Power: Utilizing wind turbines to generate electricity. Hydropower: Producing energy from flowing water. Energy Efficiency Measures Building Insulation: Reducing energy consumption in heating and cooling. Energy-Efficient Appliances: Using devices that consume less power. Sustainable Transportation Public Transit: Encouraging use of buses, trains, and other public transportation. Electric Vehicles: Reducing reliance on fossil fuel-powered cars. Biking and Walking: Promoting non-motorized transport options. Preventive Measures Policy Interventions Carbon Pricing: Implementing taxes or cap-and-trade systems to reduce emissions. Subsidies for Green Technologies: Financial support for renewable energy and efficiency projects. Regulations: Setting emission standards for industries and vehicles. Individual Actions Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Minimizing waste and promoting recycling. Dietary Changes: Adopting plant-based diets to lower carbon footprints. Conservation Practices: Reducing water and energy consumption at home. Personal Stories or Case Studies Successful Carbon Reduction Projects Community Solar Initiatives: Local solar panel installations reducing communal carbon footprints. Corporate Sustainability Programs: Businesses adopting green practices and reducing emissions significantly. Individual Efforts Eco-friendly Lifestyles: Stories of individuals drastically reducing their carbon footprints through lifestyle changes.