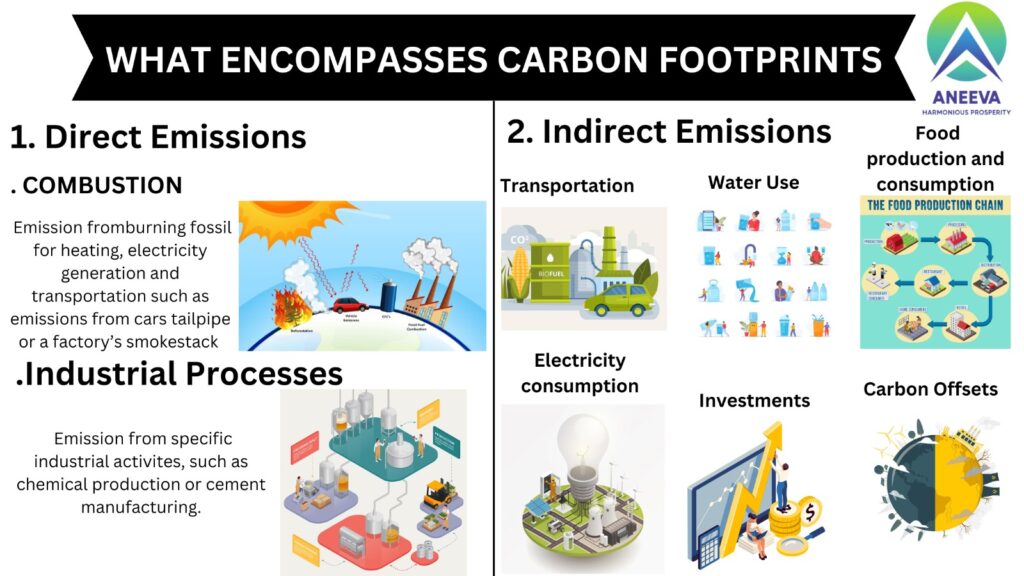
A carbon footprint encompasses a wide range of activities, processes, and sources that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
The components that can constitute a carbon footprint include:
- Energy Use: The energy consumed for heating, cooling, lighting, and operating appliances in homes, businesses, and industrial facilities is a significant contributor to carbon footprints. This includes electricity generated from fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) and renewable sources (solar, wind, hydro).
- Transportation: Emissions from vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, airplanes, ships, and trains, are a major component of carbon footprints. This includes emissions from fuel combustion and the manufacturing of vehicles.
- Industrial Processes: The manufacturing and production of goods and materials, particularly those reliant on energy-intensive processes and fossil fuel combustion. Consequently contributes to carbon footprints. These emissions include those from factories, refineries, and chemical processes.
- Agriculture and Land Use: Agriculture is a source of emissions, primarily due to methane release by livestock and the use of synthetic fertilizers. Moreover deforestation and land-use changes also contribute to carbon footprints by releasing stored carbon in forests and soils.
- Waste and Landfills: The decomposition of organic waste in landfills produces methane emissions. However production, transportation, and disposal of waste also contribute to carbon footprints.
- Consumption and Lifestyle Choices: The goods and services we consume, including food, clothing, electronics, and more, all have associated carbon footprints. This includes the emissions from manufacturing, transportation, and disposal of products.
- Construction and Building Materials: The construction and maintenance of buildings generate emissions, primarily through energy use and materials production. The choice of building materials and energy-efficient design can influence carbon footprints.
- Travel and Commuting: Business travel, commuting to work, and personal travel choices contribute to carbon footprints. This includes emissions from driving, flying, and public transportation.
- Electricity Generation: The carbon footprint of electricity generation depends on the energy mix used by power plants. Coal and natural gas power plants have higher emissions compared to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Energy and emissions are associated with the treatment of water and wastewater.
- Supply Chains: Businesses and products may have emissions associated with their supply chains, including the transportation of raw materials and finished goods.
